Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
土井 大輔; 清野 裕; 宮原 信哉*; 宇埜 正美*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(2), p.198 - 206, 2022/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Non-premixed combustion of hydrogen jets containing sodium vapor and mist reduces threats to reactor containment integrity in sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs) because it gradually consumes hydrogen gas generated mainly by a reaction between sodium and concrete. Previous studies have been limited to experimentally determining ignition thresholds on the jet temperature and the sodium concentration under specific gas concentrations. In this study, ignition experiments on hydrogen jets containing sodium mist were carried out at a specific jet temperature and sodium concentration under various gas concentration conditions (1-15vol% hydrogen and 3-21vol% oxygen). As a result, a stable sodium flame was observed in the jet and then formed a lifted hydrogen flame from a fuel nozzle outlet. An attached hydrogen flame on the outlet was also formed under high hydrogen concentration conditions. These flame structures seemed to be attributed to hydrogen flame propagation, which depends on the hydrogen concentration, jet temperature, and jet velocity. Additionally, the experimental results revealed ignition thresholds on the gas concentration and indicated a flammable region where the hydrogen-sodium jet combustion was more advantageous than an explosive premixed hydrogen combustion. Our study will enable the advancement of safety assessment technology in SRFs.
古山 大誠*; Thwe Thwe, A.; 勝身 俊之; 小林 秀昭*; 門脇 敏
日本機械学会論文集(インターネット), 87(898), p.21-00107_1 - 21-00107_12, 2021/06
断熱および非断熱条件下での水素-空気希薄予混合火炎の不安定挙動に及ぼす蒸気添加の影響を数値計算的に調査した。8つの活性種と希釈剤の17の可逆反応でモデル化された水素-酸素燃焼の詳細な化学反応メカニズムを採用し、圧縮性ナビエ・ストークス方程式に基づいて、2次元の非定常反応流が処理された。蒸気の追加と熱損失が増加すると共に平面火炎の伝播速度は減少した。水蒸気濃度の増加と共に、標準化したセル状火炎の燃焼速度は増大し、熱損失が存在する場合、標準化したセル状火炎の燃焼速度は、断熱の場合より大きくなった。水蒸気添加により、水素-空気希薄予混合火炎の不安定挙動はプロモートされる。これは、ガスの熱拡散率が減少し、拡散-熱的不安定性が強くなるからである。水素予混合火炎の不安定性に及ぼす水蒸気添加の効果は新たな知見であり、原子力発電所などにおける水素防爆対策に繋がることが期待される。
勝身 俊之; 吉田 康人*; 中川 燎*; 矢澤 慎也*; 熊田 正志*; 佐藤 大輔*; Thwe Thwe, A.; Chaumeix, N.*; 門脇 敏
Journal of Thermal Science and Technology (Internet), 16(2), p.21-00044_1 - 21-00044_13, 2021/00
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:36.79(Thermodynamics)水素/空気予混合火炎の動的挙動の特性に及ぼす二酸化炭素と水蒸気の添加の影響を実験的に解明した。シュリーレン画像により、火炎面の凹凸が低い当量比で明瞭に観察された。火炎半径が大きくなると共に伝播速度は単調に増加し、火炎面の凹凸の形成に起因する火炎加速が生じた。不活性ガスの添加量を増やすと、特にCO 添加の場合、伝播速度が低下した。さらに、マークスタインの長さと凹凸係数が減少した。これは、CO
添加の場合、伝播速度が低下した。さらに、マークスタインの長さと凹凸係数が減少した。これは、CO またはH
またはH Oの添加が水素火炎の不安定な動きを促進したことを示してあり、拡散熱効果の強化が原因であると考えられる。水素火炎の動的挙動の特性に基づいて、火炎加速を含む伝播速度の数学モデルで使用されるパラメータが得られ、その後、さまざまな条件下での火炎伝播速度が予測された。
Oの添加が水素火炎の不安定な動きを促進したことを示してあり、拡散熱効果の強化が原因であると考えられる。水素火炎の動的挙動の特性に基づいて、火炎加速を含む伝播速度の数学モデルで使用されるパラメータが得られ、その後、さまざまな条件下での火炎伝播速度が予測された。
Trianti, N.; 茂木 孝介; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2020/08
The computational fluid dynamics (CFD) have been developed to analyze the correlation equation for laminar flame speed of hydrogen-air mixtures. This analysis was carried out on the combustion of hydrogen-air mixtures performed at the spherical bomb experiment facility consists of a spherical vessel equipped (563 mm internal diameter). The facility has been designed and built at CNRS-ICARE laboratory. The simulation was carried out using the reactingFoam solver, one of a transient chemical reaction solver in OpenFOAM 5.0. The LaunderSharmaKE model was applied for turbulent flow. The interaction of the chemical reaction with the turbulent flow was taken into account using PaSR (Partial Stirred Reactor) model with 19 elementary reactions for the hydrogen combustion. The initial condition of spherical flame analysis was set so as to be consistent with those of the experiment. The position of the flame front was detected by the steep drop of hydrogen mass fraction in the spherical radii, and the flame propagation velocity was estimated from the time-position relationship. The analysis result showed the characteristic of spherical flame acceleration was qualitatively reproduced even though it has a discrepancy with the experiment. After validating the calculation of spherical experiments, a laminar burning velocity correlation is presented using the same boundary conditions with the variation of hydrogen concentration, temperature, and pressure. The calculation of laminar flame speed of hydrogen-air mixtures by reactingFoam use reference temperature T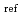 = 293 K and reference pressure P
= 293 K and reference pressure P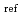 = 1 atm with validated in the range of hydrogen concentration 6-20%; range of temperature 293-493 K; and range of pressure 1-3 atm.
= 1 atm with validated in the range of hydrogen concentration 6-20%; range of temperature 293-493 K; and range of pressure 1-3 atm.
茂木 孝介; Trianti, N.; 松本 俊慶; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.4324 - 4335, 2019/08
Hydrogen managements under severe accidents are one of the most crucial problems and have attracted a great deal of attention after the occurrence of hydrogen explosions in the accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in March 2011. The primary purpose of our research is improvements in computational fluid dynamics techniques to simulate hydrogen combustion. Our target of analysis is ENACCEF2 hydrogen combustion benchmark test conducted in the framework of ETOSON-MITHYGENE project. Flame acceleration experiments of hydrogen premixed turbulent combustions were simulated by the Turbulent Flame Closure (TFC) model. We implemented several laminar flame speed correlations and turbulent flame speed models on XiFoam solver of OpenFOAM and compared the results to investigate the applicability of these correlation and model equations. We found that all the laminar flame speed correlations could predict qualitative behavior of the flame acceleration, but Ravi & Petersen laminar flame speed correlation that is originally implemented in OpenFOAM underestimated the maximum flame speed for the lean hydrogen concentration. Zimont model and G lder model of the turbulent flame speed could reasonably simulate the flame acceleration behavior and maximum pressure peaks. The flame velocities calculated with G
lder model of the turbulent flame speed could reasonably simulate the flame acceleration behavior and maximum pressure peaks. The flame velocities calculated with G lder model tend to be faster than that calculated with Zimont model.
lder model tend to be faster than that calculated with Zimont model.
土井 大輔; 清野 裕; 宮原 信哉*; 宇埜 正美*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(6), p.521 - 532, 2019/06
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:11.15(Nuclear Science & Technology)In severe accident scenarios for sodium-cooled fast reactors, it is desirable to gradually consume hydrogen generated by various ex-vessel phenomena without posting a challenge to containment integrity. An effective means is combustion of hydrogen jets containing sodium vapor and mist, but previous studies have been limited to determining ignition thresholds experimentally. The aim of this study was to visualize the ignition process in detail to investigate the ignition mechanism of hydrogen-sodium mixed jets. The ignition experiments of the hydrogen jet containing sodium mist were carried out under a condition of little turbulence. The ignition process was measured with an optical measurement system comprised of a high-speed camera and an image intensifier, and a spatial distribution of luminance was analyzed by image processing. Detail observation revealed that sodium mist particles burned as scattering sparks inside the jet and that hydrogen ignited around the mist particles. Additionally, the experimental results and a simple heat balance calculation indicated that the combustion heat of sodium mist particles could ignite the hydrogen as the heterogeneous ignition source in the fuel temperature range where the mist particle formation was promoted.
Thwe Thwe, A.; 寺田 敦彦; 日野 竜太郎
JAEA-Technology 2018-012, 45 Pages, 2019/01
原子力発電所に関連するシビアインシデントや製造工程のリスク以外に、原子力廃棄物のリスクも社会を脅かす可能性がある。低レベル及び高レベルの放射性廃棄物を含む核廃棄物の長期保管下では、金属廃棄物の腐食や容器壁自体の腐食及び廃棄物中の水の放射線分解により水素が自発的に発生する。そこで、水素安全及び環境汚染のリスク低減のために、放射性廃棄物容器における水素燃焼爆発の挙動と特性を調べることとした。本報告書では、OpenFOAMを適用し、簡易コンテナー内におけるメタン燃焼の温度, 速度と二酸化炭素分布を調べる数値解析シミュレーションを行った。燃焼シ解析では、LESフレームを備えているFireFoamソルバーを使用した。結果として、容器の高さ及び流入口のサイズが大きくなるとともに平均温度が上昇することが分かった。一方、FireFoamソルバーで行ったメタン、水素及びヘリウムの拡散挙動シミュレーションから、メタンや水素よりもヘリウムのほうが速く拡散することが明らかにした。XiFoamソルバーを利用することにより、化学量論的条件下で立方体燃焼容器における水素空気予混合火炎の火炎伝播半径が得られた。
Bentaib, A.*; Chaumeix, N.*; Grosseuvres, R.*; Bleyer, A.*; Gastaldo, L.*; Maas, L.*; Jallais, S.*; Vyazmina, E.*; Kudriakov, S.*; Studer, E.*; et al.
Proceedings of 12th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-12) (USB Flash Drive), 11 Pages, 2018/10
In the framework of the French MITHYGENE project, the new highly instrumented ENACCEF2 facility was built at the Institut de Combustion Aerothermique Reactivite et Environnement (ICARE) of the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) in Orleans (France) to address the flame propagation in hydrogen combustion during a severe accident. The ENACCEF2 facility is a vertical tube of 7.65 m height and 0.23 m inner diameter. In the lower part of the tube, annular obstacles are installed to promote turbulent flame propagation. At the initiative of the MITHYGENE project consortium and the European Technical Safety Organisation Network (ETSON), a benchmark on hydrogen combustion was organised with the goal to identify the current level of the computational tools in the area of hydrogen combustion simulation under conditions typical for safety considerations for NPP. In the proposed paper, the simulation results obtained by participating organizations, using both Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) and lumped-parameter computer codes, are compared to experimental results and analysed.
松本 俊慶; 佐藤 允俊; 杉山 智之; 丸山 結
Proceedings of 25th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-25) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2017/07
Hydrogen combustion including deflagration and detonation could become a significant threat to the integrity of containment vessel or reactor building in a severe accident of nuclear power stations. In the present study, numerical analyses were carried out for the ENACCEF No.153 test to develop computational techniques to evaluate the flame acceleration phenomenon during the hydrogen deflagration. This experiment investigated flame propagation in the hydrogen-air premixed gas in a vertical channel with flow obstacles. The reactingFoam solver of the open source CFD code, OpenFOAM, was used for the present analysis. Nineteen elementary chemical reactions were considered for the overall process of the hydrogen combustion. For a turbulent flow, renormalization group (RNG) k-e two-equation model was used in combination with wall functions. Three manners of nodalization were applied and its influences on the flame propagation acceleration were discussed.
稲葉 良知; 西原 哲夫; 森山 耕一*; 中村 正志*
JAERI-Data/Code 2002-014, 255 Pages, 2002/07
高温ガス炉(HTGR)を用いた水素製造システムでは、原子炉に水素製造プラントを接続し、多量の可燃性流体を取り扱うことになるが、これによって原子炉の安全性が低下することがあってはならず、特に火災・爆発事故対策は安全上最も重要な課題の1つである。現在、日本原子力研究所では、高温工学試験研究炉(HTTR)に接続する天然ガスを用いた水蒸気改質法による水素製造システムを計画中である。そこで、実用規模HTGR水素製造システムへの適用までを視野に入れた火災・爆発事故対策を検討し、HTGR水素製造システム及びHTTR水素製造システムで想定される火災・爆発事故について、事象推移と影響を詳細に解析するためのコードシステムP2Aを開発した。P2Aは、原子炉建家内外部における可燃性流体の漏洩,移流拡散,着火,燃焼(爆燃及び爆ごう)の過程を解析することができる。本報告書では、P2Aコードシステムが解析対象とする施設,事象やコードシステムの概要,使用方法及び予備計算結果について述べる。
稲葉 良知; 西原 哲夫; 稲垣 嘉之
Proceedings of 14th Hydrogen Energy Conference (WHEC 2002) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2002/06
現在、日本原子力研究所では、高温工学試験研究炉(HTTR)に接続する天然ガスを用いた水蒸気改質法による水素製造システムを計画中である。HTTR水素製造システムにおいて、火災・爆発対策は安全上、最も重要な課題の1つである。そこで、HTTR水素製造システムで想定される火災・爆発事故について、事象推移と影響を詳細に解析するためのコードシステムP2Aを開発した。P2Aは、原子炉建家内外部における可燃性流体の漏洩,移流拡散,燃焼(爆燃及び爆ごう)の過程を解析することができる。本研究では、P2Aの概要及び予備計算結果について述べる。
Thwe Thwe, A.; 寺田 敦彦; 日野 竜太郎
no journal, ,
高レベル放射性含水廃棄物容器中に水素が継続的に発生しているので、水素の燃焼と爆発の危険性について注意する必要がある。水素安全管理においては、実験的な研究に加え、火炎伝播現象の予測におけるCFDアプローチは重要な役割を果たしている。そこで、放射性廃棄物容器中の水素燃焼へのアプローチとして、オープンソースソフトウェア、OpenFOAMを用いて、水素-空気予混合火炎伝播シミュレーションを行った。勝身ら[長岡技術科学大学]による水素-空気爆発実験から導き出された新しい層流火炎速度モデルをXiFoamソルバーに実装したシミュレーションでは、実験と同じく火炎が外側に広がったときにしわ状火炎が形成され、シミュレーションから得られた球状火炎半径は実験結果と0.005秒以内の差でよく一致した。